|
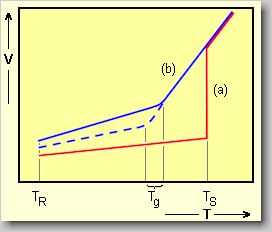
Changing of volume of a
melt during cooling,
(a) caused by crystallization,
(b) caused by formation
of glass.
Crystalline materials go
through an enormous variation in volume with the melting temperature TS,
they crystallize (red line). In contrast to crystalline materials glasses
condense over a wide temperature range (blue curve) also beyond TS.
In the area of the transformation temperature Tg they change
from the plastic state to the brittle state when cooled slowly (blue doted
line). Rapid cooling leads to an undercooled liquid (blue line).
TR = ambient temperature,
Tg = transformation
temperature,
TS = melting
point. |